Speed
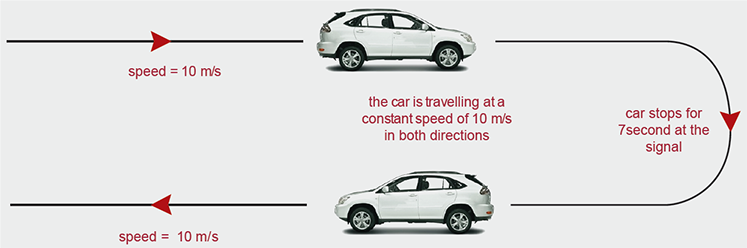
Distance travelled per unit time is speed.

Speed is a scalar quantity because it has magnitude but it does not have a direction.
Distance is measured in metres (m), time is measured in seconds (s), speed is measured in metres per second (m/s).
Other Units for Speed
The SI Units to use for speed in science is metres per second (m/s) but there are others that you use in everyday life.
- kilometers per hour (km/h)
- Miles per hour (miles/h or m.p.h.)
The Magic Triangle for Speed, Distance and Time

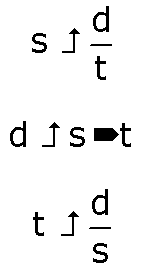
Measuring Speed by an Experiment
If we want to calculate how fast a bicycle is moving, we have to measure the distance travelled and time taken.
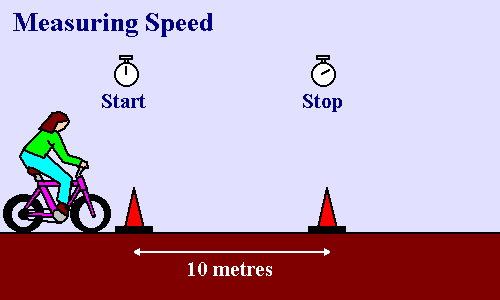
Mark out a measured distance with two markers - say 10 m.
Ask the cyclist to ride the bicycle between the two markers.
Start a stopwatch as she passes the first marker and stop the stopwatch as she passes the second marker.
Measurements
Distance travelled = 10 m
Time taken = 0.8 s
Calculation

Average Speed
Average speed can be calculated by dividing the total distance travelled by the total time that has been taken. It is defined as:
Total distance travelled divided by total time taken is called average speed.

Velocity
Displacement per unit time is called velocity.

Velocity is a vector quantity. Velocity has a magnitude and a direction as well.